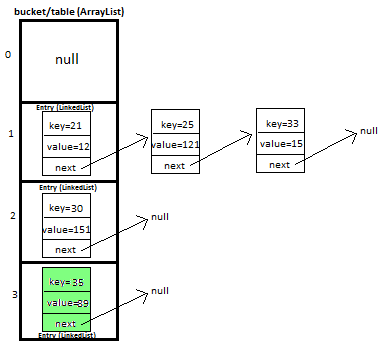
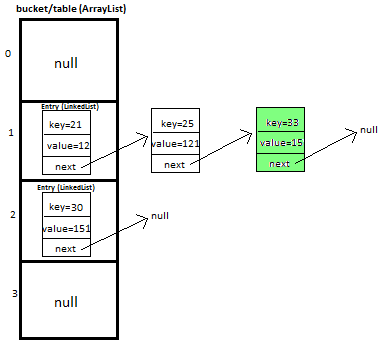
I will be explaining how we will put and get key-value pair in HashMap by overriding We will maintain bucket (ArrayList) which will store Entry (LinkedList). We store key-value pair by using Entry<K,V>,Entry contains I will explain you the whole concept of HashMap by putting 5 key-value pairs in HashMap. Initially, we have bucket of capacity=4. (all indexes of bucket i.e. 0,1,2,3 are pointing to null) Let’s put first key-value pair in HashMap,Key=21, value=12,newEntry Object will be formed like this We will calculate hash by using our hash(K key) method - in this case it returns key%capacity = 21%4= 1. So, 1 will be the index of bucket on which newEntry object will be stored. Let’s put second key-value pair in HashMap: Key=25, value=121 , newEntry Object will be formed like this: key%capacity= 25%4= 1 Let’s put third key-value pair in HashMap:Key=30, value=151,newEntry Object will be formed like this We will calculate hash by using our hash(K key) method - in this case it returns At completion of this step, our HashMap will look like this: Let’s put fourth key-value pair in HashMap: Key=33, value=15,Entry Object will be formed like this At completion of this step our HashMap will look like this https://www.javamadesoeasy.com/2015/02/hashmap-custom-implementation.html
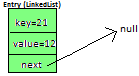
Entry<K,V>
static class Entry<K, V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
public Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> next){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
Putting 5 key-value pairs
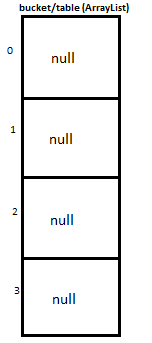
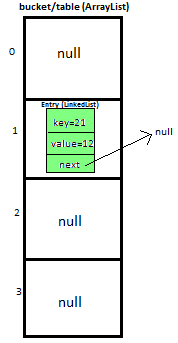
第一步
We will go to 1st index as it is pointing to null we will put our newEntry object there.
At completion of this step, our HashMap will look like this:
第二步
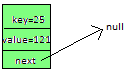
We will calculate hash by using our hash(K key) method - in this case it returns
So, 1 will be the index of bucket on which newEntry object will be stored. We will go to 1st index, it contains entry with key=21, we will compare two keys(i.e. compare 21 with 25 by using equals method), as two keys are different we check whether entry with key=21’s next is null or not, if next is null we will put our newEntry object on next.
At completion of this step our HashMap will look like this
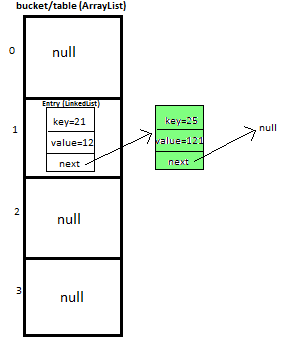
第三步
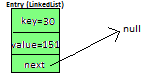
key/capacity= 30%4= 2. So, 2 will be the index of bucket on which newEntry object will be stored. We will go to 2nd index as it is pointing to null we will put our newEntry object there.
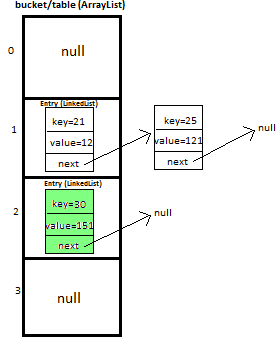
第四步
We will calculate hash by using our hash(K key) method - in this case it returns
key/capacity= 33%4= 1, So, 1 will be the index of bucket on which newEntry object will be stored.
We will go to 1st index
完整代码
package com.ankit;
/**
* @author AnkitMittal, JavaMadeSoEasy.com
* Copyright (c), AnkitMittal . All Contents are copyrighted and must not be
* reproduced in any form.
* This class provides custom implementation of HashMap(without using java api's)-
* which allows us to store data in key-value pair form.
* insertion order of key-value pairs is not maintained.
* @param <K>
* @param <V>
*/
class HashMapCustom<K, V> {
private Entry<K,V>[] table; //Array of Entry.
private int capacity= 4; //Initial capacity of HashMap
static class Entry<K, V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
public Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> next){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public HashMapCustom(){
table = new Entry[capacity];
}
/**
* Method allows you put key-value pair in HashMapCustom.
* If the map already contains a mapping for the key, the old value is replaced.
* Note: method does not allows you to put null key though it allows null values.
* Implementation allows you to put custom objects as a key as well.
* Key Features: implementation provides you with following features:-
* >provide complete functionality how to override equals method.
* >provide complete functionality how to override hashCode method.
* @param newKey
* @param data
*/
public void put(K newKey, V data){
if(newKey==null)
return; //does not allow to store null.
//calculate hash of key.
int hash=hash(newKey);
//create new entry.
Entry<K,V> newEntry = new Entry<K,V>(newKey, data, null);
//if table location does not contain any entry, store entry there.
if(table[hash] == null){
table[hash] = newEntry;
}else{
Entry<K,V> previous = null;
Entry<K,V> current = table[hash];
while(current != null){ //we have reached last entry of bucket.
if(current.key.equals(newKey)){
if(previous==null){ //node has to be insert on first of bucket.
newEntry.next=current.next;
table[hash]=newEntry;
return;
}
else{
newEntry.next=current.next;
previous.next=newEntry;
return;
}
}
previous=current;
current = current.next;
}
previous.next = newEntry;
}
}
/**
* Method returns value corresponding to key.
* @param key
*/
public V get(K key){
int hash = hash(key);
if(table[hash] == null){
return null;
}else{
Entry<K,V> temp = table[hash];
while(temp!= null){
if(temp.key.equals(key))
return temp.value;
temp = temp.next; //return value corresponding to key.
}
return null; //returns null if key is not found.
}
}
/**
* Method removes key-value pair from HashMapCustom.
* @param key
*/
public boolean remove(K deleteKey){
int hash=hash(deleteKey);
if(table[hash] == null){
return false;
}else{
Entry<K,V> previous = null;
Entry<K,V> current = table[hash];
while(current != null){ //we have reached last entry node of bucket.
if(current.key.equals(deleteKey)){
if(previous==null){ //delete first entry node.
table[hash]=table[hash].next;
return true;
}
else{
previous.next=current.next;
return true;
}
}
previous=current;
current = current.next;
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* Method displays all key-value pairs present in HashMapCustom.,
* insertion order is not guaranteed, for maintaining insertion order
* refer LinkedHashMapCustom.
* @param key
*/
public void display(){
for(int i=0;i<capacity;i++){
if(table[i]!=null){
Entry<K, V> entry=table[i];
while(entry!=null){
System.out.print("{"+entry.key+"="+entry.value+"}" +" ");
entry=entry.next;
}
}
}
}
/**
* Method implements hashing functionality, which helps in finding the appropriate
* bucket location to store our data.
* This is very important method, as performance of HashMapCustom is very much
* dependent on this method's implementation.
* @param key
*/
private int hash(K key){
return Math.abs(key.hashCode()) % capacity;
}
}
/**
* Main class- to test HashMap functionality.
*/
public class HashMapCustomApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMapCustom<Integer, Integer> hashMapCustom = new HashMapCustom<Integer, Integer>();
hashMapCustom.put(21, 12);
hashMapCustom.put(25, 121);
hashMapCustom.put(30, 151);
hashMapCustom.put(33, 15);
hashMapCustom.put(35, 89);
System.out.println("value corresponding to key 21="
+ hashMapCustom.get(21));
System.out.println("value corresponding to key 51="
+ hashMapCustom.get(51));
System.out.print("Displaying : ");
hashMapCustom.display();
System.out.println("\n\nvalue corresponding to key 21 removed: "
+ hashMapCustom.remove(21));
System.out.println("value corresponding to key 51 removed: "
+ hashMapCustom.remove(51));
System.out.print("Displaying : ");
hashMapCustom.display();
}
}
/*Output
value corresponding to key 21=12
value corresponding to key 51=null
Displaying : {21=12} {25=121} {33=15} {30=151} {35=89}
value corresponding to key 21 removed: true
value corresponding to key 51 removed: false
Displaying : {25=121} {33=15} {30=151} {35=89}
*/
原文链接