MyBatis作为一款ORM框架,主要通过XML定义Object,这就难免用到反射,虽然JDK自带的反射已经方便使用,但是MyBatis依然结合业务功能,将反射功能封装成一个更加易用的包,这个包就在reflection中。 一个POJO对象拥有两类属性,对象属性以及类信息,在MyBatis中分别通过通过MetaObject和MetaClass对应上述信息。 明白了上述信息,就能理解下面MyBatis反射包中几个关键类的作用: 这里再次复习一下,MyBatis的反射使用入口是SystemMetaObject,它包含了整个反射包的基本配置。 在MyBatis的代码中,很少能看到静态类,静态工具方法等,基本都是通过对象“注入”到对应的其他对象中。这样当需要修改实现的时候,就能很好的维护。 在MyBatis中,首先使用MetaObject,MetaObject内部充当了一个简单工厂方法,用来分辨是处理Map还是处理List还是Bean, ObjectWrapper根据不同的实现,使用不同的方式获取底层的值,对于Bean来说,使用的是MetaClass, MetaClass包含了对应Bean的Class的各种元属性。其中MetaClass底层使用的Reflector对象 Reflector对象便是真正的反射实现者,其内部根据传入的Class,生成了各种信息,并且由于Class是通用的,因此MyBatis使用ReflectorFactory将其缓存起来。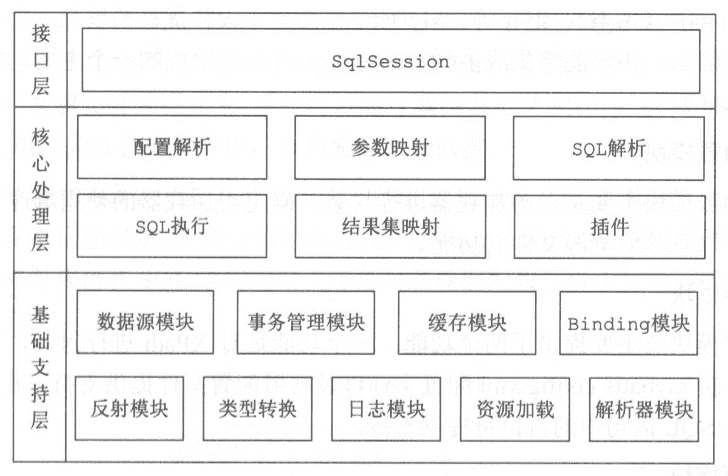
小结
ReflectorFactory 测试
public class Student {
public Integer getId() {
return 6;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
System.out.println(id);
}
public String getUserName() {
return "张三";
}
}
@Test
public void test02() throws Exception{
ReflectorFactory factory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();
Reflector reflector = factory.findForClass(Student.class);
System.out.println("可读属性:"+Arrays.toString(reflector.getGetablePropertyNames()));
System.out.println("可写属性:"+Arrays.toString(reflector.getSetablePropertyNames()));
System.out.println("是否具有默认的构造器:" + reflector.hasDefaultConstructor());
System.out.println("Reflector对应的Class:" + reflector.getType());
}
SystemMetaObject
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1);
MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(car);
Integer id = (Integer) metaObject.getValue("id");
System.out.println(" id: " + id);
原文