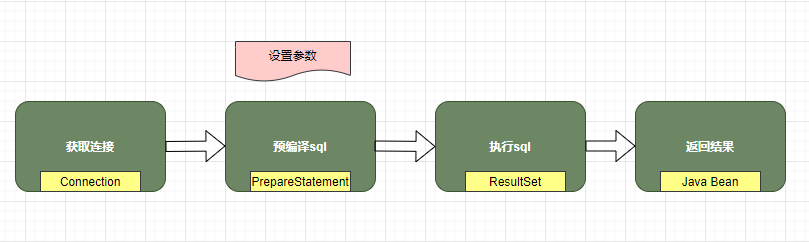
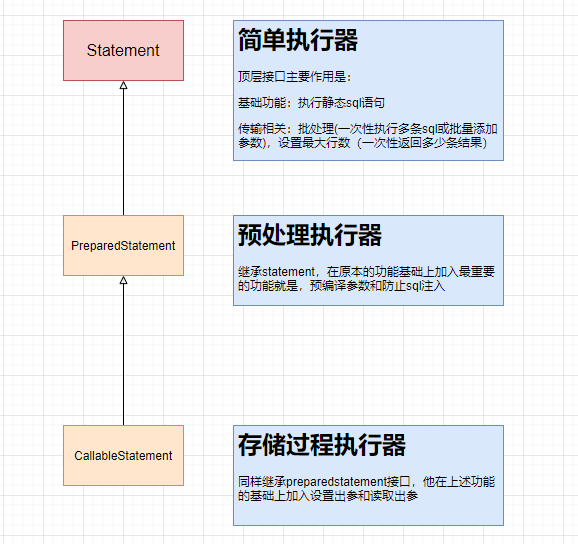
众所周知,Mybatis是对JDBC的封装,那底层肯定是JDBC,那是不是很有必要回顾一下jdbc。先写一段代码 执行过程如下图所示: 先来看看JDBC的Statement,statement的重要作用就是设置sql参数然后执行sql,先来看看jdbc的三种sql处理器: 关于防止sql注入,Statement是直接发送静态sql执行,而PreparedStatement 发送的是sql(这边会带问号)以及若干参数组,参数需要转义进去,所有的转义操作都在数据库端执行,并不是在我们的应用层转义的。 Statement 中常规方法 编码示例: 各个组件的功能以及注意事项如下图: Executor是MyBatis执行接口,执行器的功能如下: Executor有主要的三个实现子类。分别是:SimpleExecutor(简单执行器)、ReuseExecutor(重用执行器)、BatchExecutor(批处理执行器)。 SimpleExecutor是默认执行器,它的行为是每处理一次会话当中的SQl请求都会通过对应的StatementHandler 构建一个新个Statement,这就会导致即使是相同SQL语句也无法重用Statement,所以就有了(ReuseExecutor)可重用执行器 ReuseExecutor 区别在于他会将在会话期间内的Statement进行缓存,并使用SQL语句作为Key。所以当执行下一请求的时候,不在重复构建Statement,而是从缓存中取出并设置参数,然后执行。阅读源码可以知道其实里面就包含一个statementMap,执行的时候看一下是否存在,如果有了就不需要新构建statement了,这也说明为什么执行器不能跨线程调用,这会导致两个线程给同一个Statement 设置不同场景参数。 BatchExecutor 顾名思议,它就是用来作批处理的。但会将所有SQL请求集中起来,最后调用Executor.flushStatements() 方法时一次性将所有请求发送至数据库。 三个示例的代码: 这边批处理执行器想必大家觉得和上面有所不一样吧,为什么他不写查询,其实他如果写查询的话和上面的SimpleExecutor 一样,他有批处理功能,和上面jdbc的批处理一样,他是一条sql,设置多个参数过去,然后执行。而ReuseExecutor 是设置一次参数执行一次,设置一次执行一次。还是有本质的区别 前面我们所说Executor其中有一个职责是负责缓存维护,以及事务管理。上面三个执行器并没有涉及,这部分逻辑去哪了呢?别急,缓存和事务无论采用哪种执行器,都会涉及,这属于公共逻辑。所以就完全有必要三个类之上抽象出一个基础执行器用来处理公共逻辑。 BaseExecutor 基础执行器主要是用于维护缓存和事务。事务是通过会话中调用commit、rollback进行管理。重点在于缓存这块它是如何处理的? (这里的缓存是指一级缓存),它实现了Executor中的query与update方法。会话中SQL请求,正是调用的这两个方法。Query方法中处理一级缓存逻辑,即根据SQL及参数判断缓存中是否存在数据,有就走缓存。否则就会调用子类的doQuery() 方法去查询数据库,然后在设置缓存。在doUpdate() 中主要是用于清空缓存。 BaseExecutor 只有一级缓存,那二级缓存其实是在CachingExecutor,那为什么不把它和一级缓存一起处理呢?因为二级缓存和一级缓存相对独立的逻辑,而且二级缓存可以通过参数控制关闭,而一级缓存是不可以的。综上原因把二级缓存单独抽出来处理。抽取的方式采用了装饰者设计模式,即在CachingExecutor 对原有的执行器进行包装(明白点就是CachingExecutor 包含了一个Executor,这里为三大子类执行器,子类拥有父类的方法基本就是指向了父类BaseExecutor的方法),处理完二级缓存逻辑之后,把SQL执行相关的逻辑交给实际的Executor处理(交由BaseExecutor 以及其子类处理)。 从Mybatis执行过程的图中我们可以知道,SqlSession是调用Executor,从源码中可看成SqlSession实现中,其实包含一个Executor(二级缓存)。这样整个流程就串起来了,咱们以sqlsession的查询方法的selectList方法为例(因为select方法最终都会调到selectList) 如何创建会话以及如何将执行器包装成CachingExecutor又是另一个话题了 主要为了说明一下statement 这里为jdbc的statement, 假如我们用会话调用两个不同的方法,然后里面的sql是一样的,这里说的一样只是参数不同,那我们会预编译几次呢?下面代码示例 打印结果 从代码证明也就执行一次预编译。会话期间内所有的相同sql都只预编译一次即可 上面是重用执行器,预编译一次,那我们试一下批量执行器,小编前面说过,批量执行器需要使用修改的方法,那我们换一下代码: 执行结果表明,这边statement预编译一次即可 紧接着我们继续修改一下测试用例: 打印结果 从上面可有看出,相同sql语句在一起的与分开的是不一样的,只有连续相同的SQL语句并且相同的SQL映射声明,才会重用Statement,并利用其批处理功能。否则会构建一个新的Satement然后在flushStatements() 时一次执行。这么做的原因是它要保证执行顺序。跟调用顺序一致性。 MyBatis⽀持⽤插件对四⼤核⼼对象(Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler)进⾏拦截,对mybatis来说插件就是拦截器,⽤来增强核⼼对象的功能,增强功能本质上是借助于底层的 动态代理实现的,换句话说,MyBatis中的四⼤对象都是代理对象。 MyBatis所允许拦截的⽅法如下: SqlSource接口很简单,只有一个getBound方法: 它有很多实现,需要我们重点关注的是StaticSqlSource,RawSqlSource和DynamicSqlSource。在正式学习他们前,我们先了解一下Mybatis动态SQL和静态SQL的区别。 动态SQL表示这个SQL节点中含有 而静态SQL是不含以上这个节点的SQL,能直接解析得到含有占位符形式的SQL语句,而不需要根据传入的条件确定SQL,因此可以在加载时就完成解析。所在在执行效率上要高于动态SQL。 而DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource就分别对应了动态SQL和静态SQL,它们都封装了StaticSqlSource。即前两个中JDBC回顾
//首先加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//提供JDBC连接的URL
String url="jdbc:mysql://0.0.0.0:3306/xxxx";
String username="root";
String password="root";
//创建数据库的连接
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//创建一个statement执行者
String sql="SELECT * FROM biz_spot WHERE spot_id = ";
PreparedStatement statement = con.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setLong(1,11L);
//执行SQL语句
ResultSet result = statement.executeQuery();
//处理返回结果
while (result.next()){
System.out.println(result.getString("xxx") + "---" + result.getString("xxx"));
}
//关闭JDBC对象
con.close();
result.close();
statement.close();
//批量执行sql
@Test
public void prepareBatchTest() throws SQLException {
String sql = "INSERT INTO `users` (`name`,age) VALUES ('bob',18);";
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//设置最大行数
statement.setFetchSize(100);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
statement.addBatch(sql);
}
// 批处理 一次发射
statement.executeBatch();
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
statement.close();
}
//批量设置参数然后执行
@Test
public void prepareBatchTest() throws SQLException {
String sql = "INSERT INTO `users` (`name`,age) VALUES (?,18);";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setFetchSize(100);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
preparedStatement.addBatch(); // 添加批处理参数
}
preparedStatement.executeBatch(); // 批处理 一次发射
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
preparedStatement.close();
}
// sql注入测试
public int selectByName(String name) throws SQLException {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE `name`='" + name + "'";
System.out.println(sql);
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
statement.executeQuery(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.getResultSet();
int count=0;
while (resultSet.next()){
count++;
}
statement.close();
return count;
}
//PreparedStatement防止sql注入测试
public int selectByName2(String name) throws SQLException {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE `name`=?";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,name);
System.out.println(statement);
statement.executeQuery();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.getResultSet();
int count=0;
while (resultSet.next()){
count++;
}
statement.close();
return count;
}
@Test
public void injectTest() throws SQLException {
//正常情况下
System.out.println(selectByName("bob"));
//sql注入
System.out.println(selectByName("bob' or '1'='1"));
//sql注入并没作用
System.out.println(selectByName2("bob' or '1'='1"));
}
Mybatis执行过程
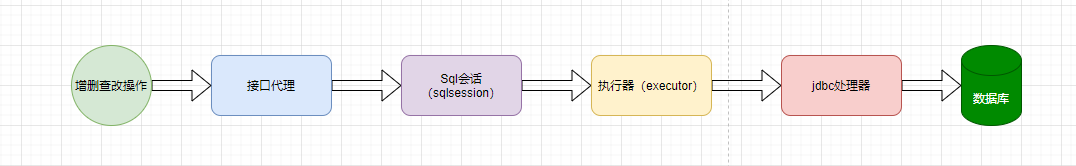
各个过程也是各个组件的作用:
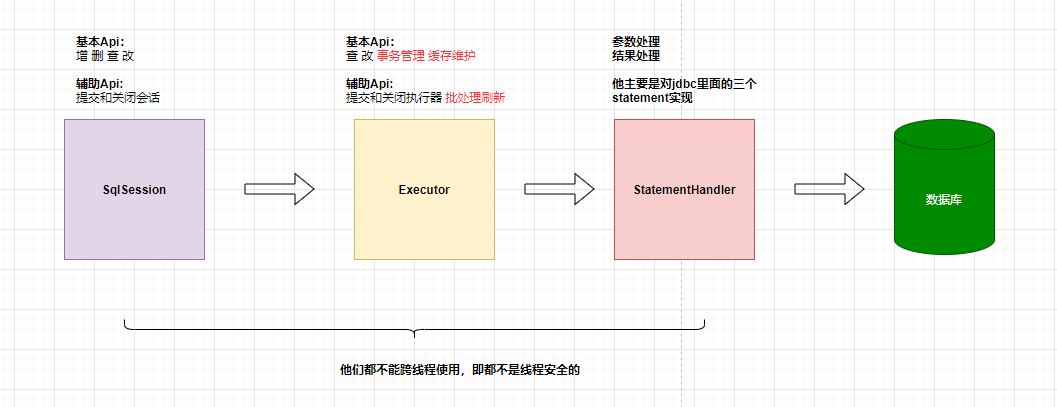
Executor
public class ExecutorTest {
private Configuration configuration;
private Connection connection;
private JdbcTransaction jdbcTransaction;
private MappedStatement ms;
private SqlSessionFactory factory;
@Before
public void init() throws SQLException {
// 获取构建器
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder factoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
// 解析XML 并构造会话工厂
factory = factoryBuilder.build(ExecutorTest.class.getResourceAsStream("/mybatis-config.xml"));
configuration = factory.getConfiguration();
jdbcTransaction = new JdbcTransaction(factory.openSession().getConnection());
// 获取SQL映射
ms = configuration.getMappedStatement("xxx.xxx.xxx.UserMapper.selectByid");
}
// 简单执行器测试
@Test
public void simpleTest() throws SQLException {
SimpleExecutor executor = new SimpleExecutor(configuration, jdbcTransaction);
List<Object> list = executor.doQuery(ms, 10, RowBounds.DEFAULT,
SimpleExecutor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER, ms.getBoundSql(10));
executor.doQuery(ms, 1, RowBounds.DEFAULT,
SimpleExecutor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER, ms.getBoundSql(1));
System.out.println(list.get(0));
}
// 重用执行器
@Test
public void ReuseTest() throws SQLException {
ReuseExecutor executor = new ReuseExecutor(configuration, jdbcTransaction);
List<Object> list = executor.doQuery(ms, 1, RowBounds.DEFAULT,
SimpleExecutor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER, ms.getBoundSql(1));
// 相同的SQL 会缓存对应的 PrepareStatement-->缓存周期:会话
executor.doQuery(ms, 1, RowBounds.DEFAULT,
SimpleExecutor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER, ms.getBoundSql(1));
System.out.println(list.get(0));
}
// 批处理执行器
@Test
public void batchTest() throws SQLException {
BatchExecutor executor = new BatchExecutor(configuration, jdbcTransaction);
MappedStatement setName = configuration
.getMappedStatement("xxx.xxx.xxx.UserMapper.setName");
Map<String,Object> param = new HashMap<>(2);
param.put("arg0", 1);
param.put("arg1", "good man");
//设置
executor.doUpdate(setName, param);
executor.doUpdate(setName, param);
executor.doFlushStatements(false);
}
}
基础以及二级缓存执行器
基础执行器
二级缓存执行器
CachingExecutor直接实现了Executor接口。Executor执行器关系图
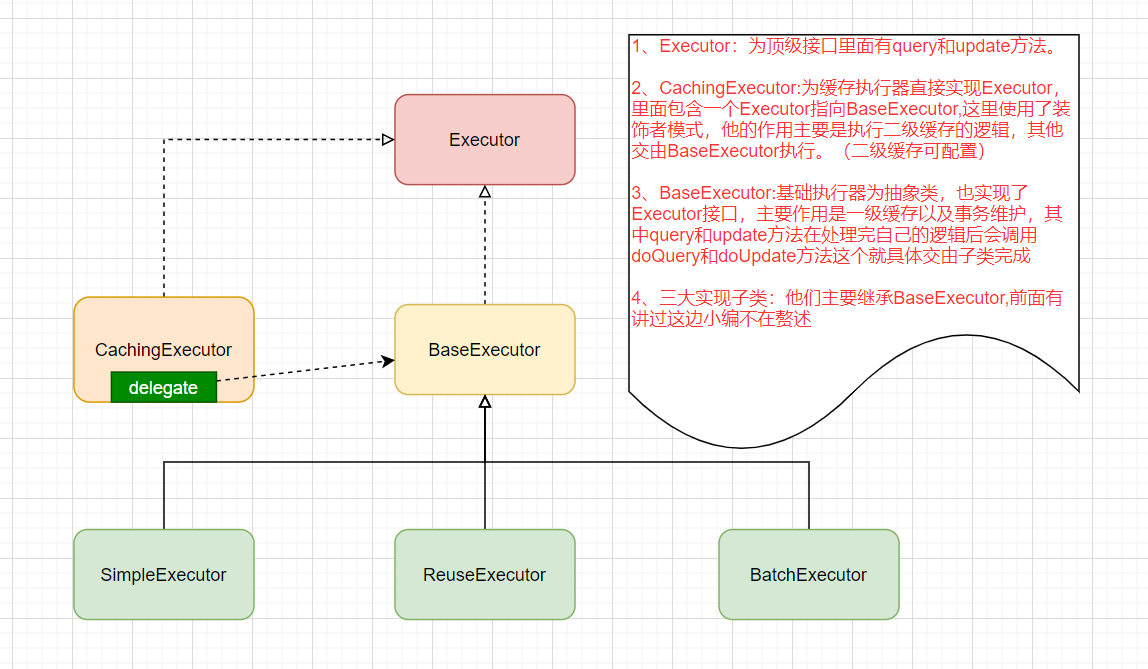
会话与执行器的结构关系
会话与重用执行器以及批量执行器的关系
重用执行器
public interface EmployeeMapper {
List<Employee> getAll();
@Select("select * from employee where id= #{id}")
List<Employee> getById(@Param("id") Long id);
@Select("select * from employee where id= #{id}")
List<Employee> selectById(@Param("id") Long id);
}
@Test
public void reuseExecutorTest() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//使用ExecutorType.REUSE设置重用执行器ReuseExecutor
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.REUSE);
try {
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
employeeMapper.selectById(1L);
employeeMapper.getById(2L);
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
==> Preparing: select * from employee where id= ?
==> Parameters: 1(Long)
<== Columns: id, name
<== Row: 1, zhangsan
<== Total: 1
==> Parameters: 2(Long)
<== Columns: id, name
<== Row: 2, lisi
<== Total: 1
批量执行器
public class DemoTest {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void batchExecutorTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH,true);
try {
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
employeeMapper.updateById("wangwu", 1L);
employeeMapper.updateById("zhaoliu",2L);
//需要走flushStatements才会提交,即便上面opensession中设置自动提交为true
List<BatchResult> batchResults = sqlSession.flushStatements();
System.out.println(batchResults.size());
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
public interface EmployeeMapper {
@Update("update employee set name = #{name} where id=#{id}")
void updateById(@Param("name")String name,@Param("id") Long id);
@Insert("insert into emplyee id = #{employee.id}, name=#{employee.name}")
void insertEmployee(@Param("employee") Employee employee);
}
==> Preparing: update employee set name = ? where id=?
==> Parameters: wangwu(String), 1(Long)
==> Parameters: zhaoliu(String), 2(Long)
1
@Test
public void batchExecutorTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH,true);
try {
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
//更新
employeeMapper.updateById("wangwu", 1L);
Employee employee = new Employee(3L,"tom");
Employee employee2 = new Employee(4L,"jerry");
//插入两次
employeeMapper.insertEmployee(employee);
employeeMapper.insertEmployee(employee2);
//再次更新
employeeMapper.updateById("zhaoliu",2L);
List<BatchResult> batchResults = sqlSession.flushStatements();
System.out.println(batchResults.size());
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
==> Preparing: update employee set name = ? where id=?
==> Parameters: wangwu(String), 1(Long)
==> Preparing: insert into employee (id,name) values (?, ?)
==> Parameters: 3(Long), tom(String)
==> Parameters: 4(Long), jerry(String)
==> Preparing: update employee set name = ? where id=?
==> Parameters: zhaoliu(String), 2(Long)
Mybatis插件
核心组件
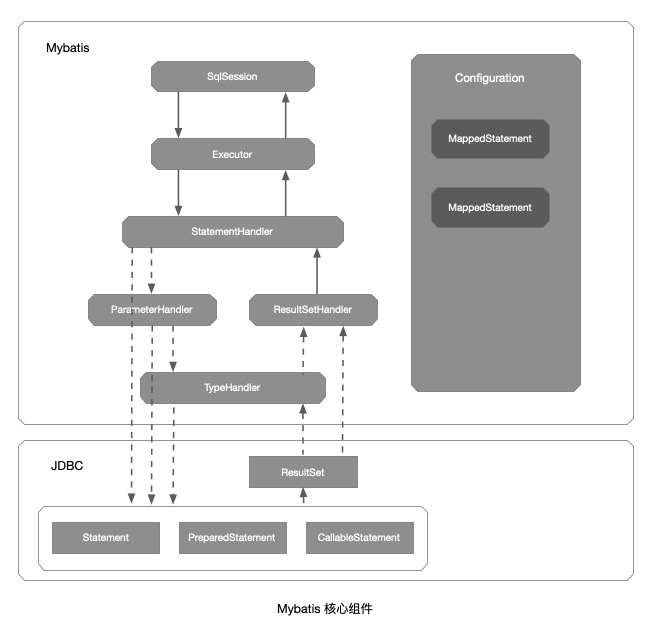
核心组件概述
组件
相关描述
Configuration
Mybatis 的主要配置。
包含属性、设置、类型别名、类型处理器、对象工厂、环境配置和映射器等信息。
MappedStatement
用于描述 Mapper 中的 SQL 配置信息。
对 Mapper XML 配置文件中 "<select
update
SqlSession
Mybatis 提供的面向用户的 API,可通过它来执行命令(增、删、改、查),获取映射器示例和管理事务。
Executor
Mybatis 的 SQL 执行器,Mybatis 中对数据库所有的增、删、改、查操作都是由它完成的。
StatementHandler
封装了对 JDBC Statement 对象的操作。
ParameterHandler
用于为 PreparedStatement 和 CallableStatement 对象参数占位符设置值。
ResultSetHandler
封装了对 JDBC 中的 ResultSet 对象操作,将 SELECT 查询结果抓换成 Java 对象。
TypeHandler
MyBatis 中的类型处理器,用于处理 Java 类型和 JDBC 类型之间的映射。
SqlSourc
public interface SqlSource {
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}
${} (不是#{}) 或是其他动态的标签(比如,if,trim,foreach,choose,bind节点等),需要在运行时根据传入的条件才能确定SQL,因此对于动态SQL的MappedStatement的解析过程应该是在运行时。getBoundSql方法是委托给StaticSqlSource对象。参考