一切的执行从MapperProxy开始,MapperProxy是MapperProxyFactory使用SqlSession创建出来的。所以MapperProxy中包含SqlSession 可以看到MapperProxy调用invoke方法,进而调用 谈原理首先要知道StatementHandler,ParameterHandler,Result Handler都是代理,他们是Configuration创建,在创建过程中会调用interceptorChain.pluginAll()方法,为四大组件组装插件(再底层是通过Plugin.wrap(target,XX, new Plugin( interceptor))来来创建的)。 在执行SqlSession的query或者update方法时,SqlSession会通过Configuration创建Executor代理,在创建过程中就调用interceptor的pluginAll方法组装插件。然后executor在调用doQuery()方法的时候,也会调用Configuration的newStatementHandler方法创建StatemenHandler(和上面描述的一样,这个handler就是个代理,也是通过interceptorChain的pluginAll方法构建插件) 以statementhandler的prepare方法的插件为例,正如前面所说,statementhandler是一个proxy,执行他的prepare方法,将调用invokeHandler的invoke方法,而invokeHandler就是Plugin.wrap(target, xxx, new Plugin(interceptor))中的第三个参数,所以很自然invokeHanlder的invoke的方法最终就会调用interceptor对象的intercept方法。 从上面的例子的getMapper()方法中点进去,一直往里跟,最后会走到org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperRegistry#getMapper这个方法。 这里可以看到我们的UserMapper是从knownMappers这个map里拿出来的,那必然是有地方放进去的,发现是通过configuration.addMapper(UserMapper.class);这行代码将UserMapper放到knownMappers中。这里实际调用的是org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperRegistry#addMapper 可以看到mybatis为我们的mapper封装了一个MapperProxyFactory对象,我们的mapper接口信息最终存在了这个对象的mapperInterface属性中,在getMapper()时,通过jdk动态代理生成代理对象,这个代理对象里面完成了对JDBC的封装,执行了真正的数据库操作。 https://www.cnblogs.com/baichunyu/p/11208524.htmlMybatis执行SQL的完整过程
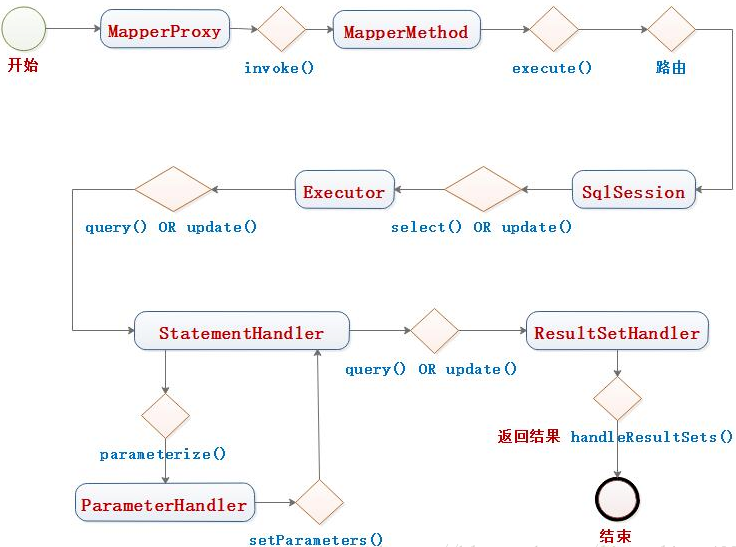
MapperMethod的execute(),这些MapperMethod 就是和你要执行的命令相关,比如执行select语句,则会通过 SqlSession的select()方法,最终调用到Executor的query方法。Executor会再协调另外三个核心组件。
MapperProxy
MapperMethod
插件的构建
插件链是何时构建的
插件如何执行
例子
package org.example;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.Environment;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.TransactionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransactionFactory;
import org.example.mapper.StudentMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
public class WithoutSpringRunner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://129.1.1.194:3386/erp?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8");
dataSource.setUsername("erp");
dataSource.setPassword("xxxxxx");
TransactionFactory transactionFactory =
new JdbcTransactionFactory();
Environment environment =
new Environment("development", transactionFactory, dataSource);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(environment);
configuration.addMapper(StudentMapper.class);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =
new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(configuration);
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
StudentMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
//这里能够执行findAll说明userMapper是一个实例,那一定是在getMapper中发生了实例化
userMapper.getAllStudent().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
}
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
原文
https://github.com/oneone1995/blog/issues/12