什么是lock-free,简单的说就是不直接使用锁,减少锁在系统中占用的开销。相比于基于锁的算法而言,Lock-free 算法具有明显的特征:某个线程在执行数据访问时挂起不会阻碍其他的线程继续执行(某个线程持有锁之后挂起,导致其他的线程没有办法申请锁)。这意味着在任意时刻,多个 lock-free 线程可以同时访问同一数据而不产生数据竞争。 上面的定义保证了 lock-free 程序中的一组线程中至少有一个可以顺利的执行而不产生阻塞,从而确保整个程序的顺利执行。lock-free中常见的就是使用cas来代替加锁。 在算法上实现非阻塞难度大,可以利用特定的数据结构实现,非阻塞数据结构可以氛围以下三类 当其他所有线程都挂起(suspended)的时候,可以保证有一个线程可以完成对共享资源的操作 More precisely, a thread won't continue to starve if all other threads are suspended. This is different from using locks in that sense, that if the thread was waiting for a lock and a thread that holds the lock is suspended, the waiting thread would wait forever. 在任意时间,至少有一个线程可以完成对共享资源的操作。 所有线程都能保证在有限的步骤或时间内,完成对共享资源的操作 Let's summarize these definitions in graphical representation: https://www.jianshu.com/p/d6eb7b58731f1. 非阻塞数据结构(Non-Blocking Data Structures)
1.1. Obstruction-Free
Obstruction-freedom is the weakest form of a non-blocking data structure. Here, we only require that a thread is guaranteed to proceed if all other threads are suspended.1.2. Lock-Free
A data structure provides lock-freedom if, at any time, at least one thread can proceed. All other threads may be starving. The difference to obstruction-freedom is that there is at least one non-starving thread even if no threads are suspended.1.3 Wait-Free
A data structure is wait-free if it's lock-free and every thread is guaranteed to proceed after a finite number of steps, that is, threads will not starve for an “unreasonably large” number of steps.1.4 Summary
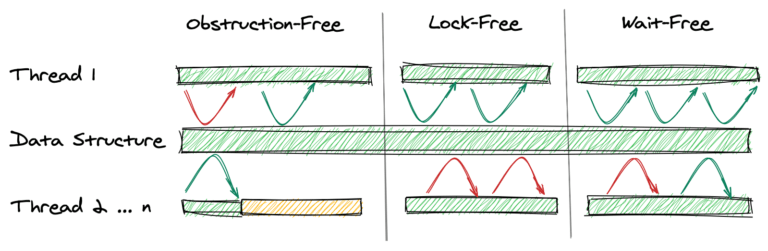
参考链接
https://www.baeldung.com/lock-free-programming
https://www.cnblogs.com/gaochundong/p/lock_free_programming.html